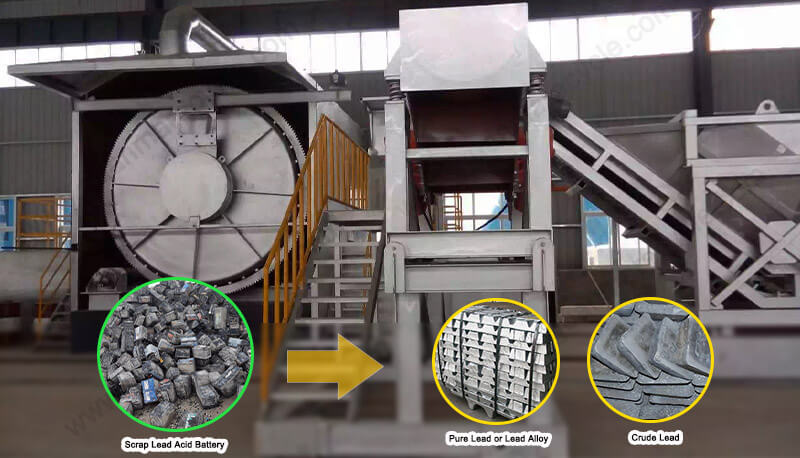
Wondering about lead acid battery recycling plant cost? For entrepreneurs and businesses looking to enter the valuable lead recycling market, understanding the investment required is crucial. The final price tag isn’t a simple number – it hinges directly on what you process, how much you handle daily, and the valuable products you aim to recover. Guanma machinery breaks down the key elements influencing your lead acid battery recycling plant cost, empowering you with realistic expectations.
What Raw Materials Will Your Plant Process?
The starting point significantly shapes your lead acid battery recycling plant cost. Primarily, you’ll handle:
1. Spent Lead-Acid Batteries (SLABs)
The core feedstock. These include:
Automotive Batteries (SLI): Common car, truck, and motorcycle batteries.
Industrial Batteries: Larger units from forklifts, telecom backup (UPS), and renewable energy storage.
VRLA Batteries: Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid batteries, common in UPS systems and some automotive applications.

2. Battery Breaking Residues
Materials generated from initial crushing/separation stages at other facilities, ready for smelting.
3. Lead Paste
Often separated at initial processing facilities, this is the active material containing lead oxides and sulfates.
Why it affects cost
Handling whole batteries requires more complex breaking, separation, and acid neutralization systems than processing pre-separated components like paste or residues. The type and condition of incoming batteries (e.g., whole vs. drained, plastic casings intact) also influence the necessary equipment sophistication and environmental controls, impacting your lead acid battery recycling plant setup cost.
What’s Your Target Daily Processing Capacity?
Scale is a major determinant of lead acid battery recycling plant cost. Capacity is typically measured in metric tons per day (MT/day) of batteries processed.
Small-Scale Plants (5 – 20 MT/day)
Ideal for regional operations or starting. Lower initial lead acid battery recycling equipment investment but higher cost per ton processed. Often semi-automated.
Medium-Scale Plants (20 – 100 MT/day)
The sweet spot for many profitable ventures. Balances significant throughput with manageable lead acid battery scrap processing plant investment. Features higher automation.
Large-Scale Plants (100+ MT/day)
Require substantial capital expenditure (large scale lead acid battery recycling facility price). Benefit from economies of scale and full automation. Need massive, consistent feedstock supply.
Cost Implication
A plant designed for 50 MT/day will have significantly higher costs for smelting furnaces, pollution control systems (like advanced baghouses and acid scrubbers), material handling conveyors, and automation/control systems than a 10 MT/day operation. Labor costs also scale, though automation reduces this per ton.

What End Products Are You Aiming For?
The sophistication of your process and the purity of your final products directly impact your lead acid battery recycling plant cost. The core recoverable materials are:
1. Lead: The primary revenue driver. Sold as:
Soft Lead Ingots: (Commonly >99.97% purity) – Used for new batteries, radiation shielding, ammunition.
Antimonial Lead Ingots: (Hard Lead) – Contains antimony for hardness, used in specific battery types and alloys.
Refined Lead (via refining kettles): Higher purity for specialized applications. Adds significant cost to set up lead acid battery recycling facility.
2. Polypropylene (PP) Plastic Chips
Recovered from battery casings. Washed and sold to plastic recyclers/manufacturers. Requires effective washing and granulation equipment.
3. Sodium Sulfate (or Gypsum)
Produced from neutralizing sulfuric acid. Requires crystallization or precipitation systems. Market value depends on purity.
Why it affects cost
Producing high-purity lead ingots demands advanced smelting furnaces (rotary, reverberatory), refining kettles, dross handling systems, and stringent quality control. Simply producing crude lead bullion is cheaper but less profitable. Efficiently recovering clean PP plastic adds separation and washing stages. Producing saleable sodium sulfate requires additional chemical processing units. Maximizing profit from recycled lead ingots and plastic requires this investment.

Key Factors Driving Lead Acid Battery Recycling Plant Cost
Beyond feedstock, capacity, and products, several other critical factors determine the final lead acid battery recycling plant cost:
Technology & Automation Level
Basic manual/semi-auto lines cost less upfront than fully automated lines with robotic handling and advanced process control, but have higher labor costs and lower efficiency. Automated lead battery recycling line price is higher but often offers better ROI long-term.
Environmental Compliance Systems
This is non-negotiable and a major cost component. Includes sophisticated fume capture (hoods, ducting), air pollution control (bag filters, wet scrubbers), wastewater treatment plants, and emission monitoring systems. Meeting stringent regulations (lead acid recycling plant environmental compliance cost) is essential but expensive.
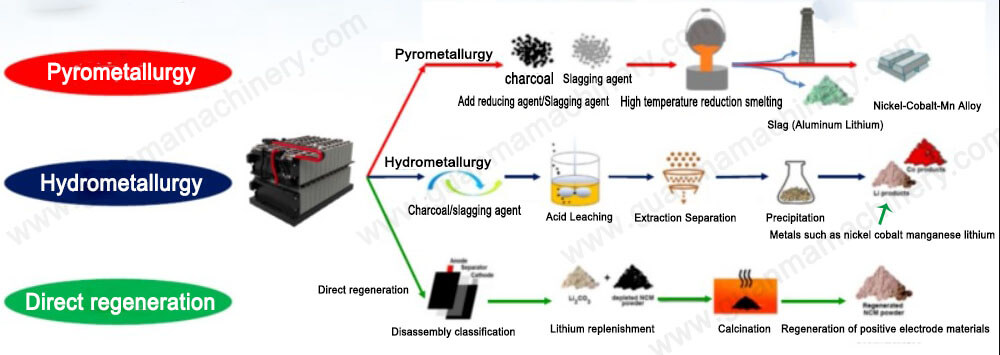
Process Choice
Pyrometallurgical (smelting) is standard but requires significant energy and emission controls. Hydrometallurgical processes (chemical leaching) are emerging, potentially offering lower emissions but often with higher chemical costs and complexity. Battery recycling plant smelting furnace cost is a major factor.
Location & Site Preparation
Costs for land, building construction/retrofitting, utility connections (high-power electricity, water), and logistics vary greatly by region. Lead recycling plant installation expenses include civil works.
Equipment Origin & Quality
Premium European/North American equipment commands higher prices than some Asian alternatives, though quality and support differ. New vs. quality used equipment is a cost/risk trade-off. Consider lead acid battery processing equipment suppliers carefully.
Engineering, Installation & Commissioning
Professional services are vital for a safe, efficient, compliant plant but add to the total turnkey lead acid battery recycling plant price.
Spare Parts & Operating Costs
Factor in ongoing costs for refractories, chemicals, energy, labor, maintenance, and compliance testing. Operating cost for lead battery recycling facility impacts profitability.
Estimated Cost Ranges (Very Indicative – Get Detailed Quotes!):
Small Scale (5-20 MT/day): $500,000 – $2.5 Million USD
Medium Scale (20-100 MT/day): $2 Million – $10 Million USD
Large Scale (100+ MT/day): $10 Million – $50 Million+ USD
FAQ: Lead Acid Battery Recycling Plant Costs
Q1: What is the typical lead acid battery recycling plant cost range?
A: Costs vary enormously based on scale, technology, and location. Expect $500,000 USD for very small, basic setups up to $50 million USD or more for large, fully automated, compliant facilities. Medium-scale plants (20-100 MT/day) often range between $2 million and $10 million USD.
Q2: How long does it take to set up a lead acid battery recycling plant?
A: From initial planning to commissioning, expect 18 to 36 months. This includes feasibility studies, permitting (which can be lengthy), detailed engineering, equipment manufacturing/delivery, construction, installation, and rigorous commissioning/testing. Timeline for establishing a battery recycling facility depends heavily on permitting and equipment lead times.
Q3: Can I get a lower cost by buying used equipment?
A: Yes, quality used equipment can offer significant savings on lead recycling machinery cost. However, this requires expert evaluation of the equipment’s condition, remaining lifespan, technological relevance, and compatibility. Factor in potential refurbishment costs and potentially higher maintenance/downtime risks. Ensure it meets current environmental standards.
Q4: What are the biggest ongoing operating costs?
A: Key operational expenses for battery recycling plants include:
Energy: Smelting is energy-intensive (electricity, natural gas, coke).
Labor: Skilled operators and maintenance staff.
Consumables: Refractory linings for furnaces, process chemicals, filter bags.
Environmental Compliance: Emission monitoring, waste disposal (dross, residues), wastewater treatment chemicals.
Maintenance & Repairs: Keeping complex machinery running.
Feedstock Acquisition: Cost of purchasing spent batteries.
Q5: How quickly can a lead acid battery recycling plant become profitable?
A: Profitability depends heavily on efficient operations, consistent high-quality feedstock supply, recovered metal/plastic market prices, effective cost control, and scale. Well-run medium-to-large scale plants can achieve profitability within 2-5 years after commissioning, though this is highly variable. ROI on lead battery recycling investment is sensitive to lead prices and operational efficiency.
Understanding lead acid battery recycling plant cost is the first strategic step. By clearly defining your processing goals (materials, daily volume, end products) and carefully evaluating the key cost drivers – technology, compliance, scale, and location – you can make informed investment decisions. Partnering with experienced technology providers who offer tailored solutions and transparent costing is crucial for building a profitable and sustainable operation in this vital recycling sector.