Setting up a lead-acid battery recycling plant is a crucial step towards sustainable resource recovery and a potentially profitable business venture. However, understanding the main cost factors is essential for realistic budgeting and long-term success.
1. Plant Scale & Processing Technology:
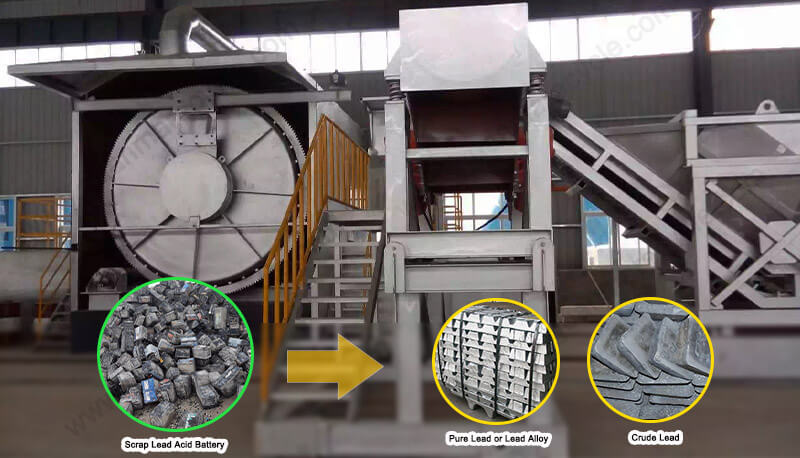
The core cost driver is the plant’s capacity (tons processed per day) and the technology chosen. Options range from basic manual breaking units to fully automated battery recycling lines.
Equipment Costs: This is typically the largest CAPEX component (40-60%). Key machinery includes:
Battery Breaker & Separator System: Crucial for separating lead, plastic, and acid. Costs vary significantly based on automation level (hammer mill vs. rotary crusher prices).
Smelting Furnace: The heart of lead recovery (lead smelting furnace cost, rotary vs. blast furnace). Emissions control systems (baghouses, scrubbers – emission control system investment) are major add-ons.

Refining & Alloying: Kettles, refining pots, dross handling systems.
Plastic Washing & Pelletizing Line: For recycling polypropylene cases.
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP): Mandatory for neutralizing and treating sulfuric acid (battery acid neutralization plant cost).
Automation Level: Higher automation increases initial cost but drastically reduces labor needs and boosts efficiency/safety long-term.
2. Site Acquisition, Preparation & Construction:
Land Cost: Requires significant space for processing, storage, and potential expansion.
Site Preparation: Ground leveling, foundations, drainage, utilities (heavy power supply, water connections -industrial power supply for recycling plant).
Building Construction: Weatherproof structures for operations, offices, labs, and hazardous material storage.
3. Permitting, Compliance & Environmental Controls:
Meeting stringent environmental regulations for battery recycling is non-negotiable and costly.
Permitting Fees: Air emissions, wastewater discharge, hazardous waste handling permits.
Engineering & Design: Specialized engineering for plant layout meeting OSHA, EPA, and local codes.
Advanced Pollution Control: Beyond basic requirements (e.g., advanced scrubbers, continuous emission monitoring systems – CEMS cost for lead smelter) add significant expense.
Safety Systems: Fire suppression, ventilation, PPE, monitoring equipment.

4. Raw Material Logistics & Collection Network:
Securing a steady supply of scrap lead-acid batteries is vital.
Collection Infrastructure: Setting up drop-off points, partnerships with retailers/auto shops, or establishing a dedicated collection fleet (scrap battery transportation logistics cost).
Purchasing Price: Fluctuates based on lead market prices and local competition.
5. Manpower & Expertise:
Skilled Labor: Requires trained operators, metallurgists, chemists, maintenance engineers, and EHS personnel (specialized labor for battery recycling).
Training Costs: Extensive safety, environmental compliance, and process training are mandatory.
Salaries & Benefits: Competitive packages are needed for specialized roles.
6. Utilities & Operational Consumables:
High Energy Consumption: Smelting furnaces are energy-intensive (electricity cost for lead refining is a major OPEX factor). Natural gas or other fuels also contribute.
Water: Used in cooling, acid neutralization, and plastic washing.
Chemicals: Neutralizing agents (e.g., soda ash), fluxes for smelting, water treatment chemicals.
Refractories: Lining materials for furnaces require regular replacement.
7. Working Capital & Contingency:
Buffer Funds: Cover initial operating expenses before revenue stabilizes and manage fluctuations in scrap battery purchase costs or lead sales prices.
Contingency Fund: Essential for unexpected delays, cost overruns, or equipment issues (typically 10-15% of project cost).
Maximizing ROI: Key Considerations
Byproduct Revenue: Efficient plastic and sodium sulfate (from acid neutralization) recycling generates significant secondary income streams (profit from recycled battery plastic).
Scale Economies: Larger plants generally have lower processing costs per ton.
Technology Choice: Balance upfront cost with long-term efficiency, yield, and environmental compliance. Cutting corners here is risky.
Location: Proximity to battery scrap sources and lead consumers reduces logistics costs.
A Strategic Investment
Understanding these primary cost factors in lead-acid battery recycling plant setup is fundamental. While the initial investment is substantial, driven by advanced recycling equipment expenses and strict environmental compliance costs, a well-planned facility offers strong returns through efficient resource recovery and growing market demand for recycled lead and plastics. Careful analysis of each cost component, technology selection, and robust operational planning are the cornerstones of building a profitable and sustainable lead recovery business.




